This is the third post on the results of the Java survey I ran recently. If you haven’t seen the first two, you’ll find them here and here. In this post we’ll be covering application servers.
What’s an application server?
There are a few options to run web applications in Java.
Web applications that use Java Enterprise Edition code (EJBs) need to deploy to a full-fledged JEE application server (Websphere, Weblogic, etc.).
Web applications that don’t use EJBs can be also deployed to a more lightweight web container (Tomcat, Jetty, etc.).
And if you’re using one of the latest Java web frameworks, you may not need a container at all (Vert.x or Play framework) or use an embedded one (Spring Boot).
Most commonly used application servers
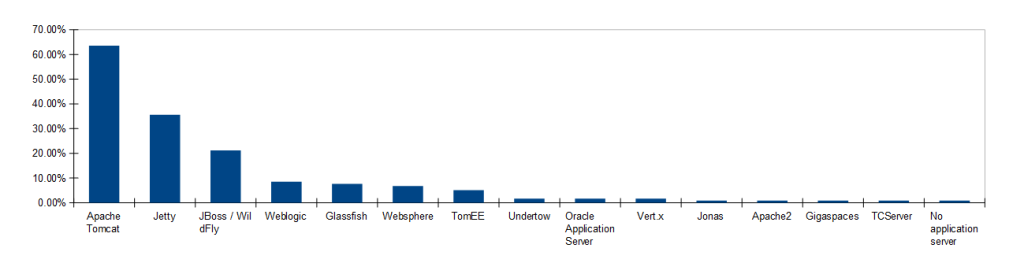
See below the list of application servers from the java survey results:
- Apache Tomcat – an open-source web server that powers numerous large-scale, mission-critical web applications across a diverse range of industries and organizations
- Jetty – a Java HTTP (Web) server and Java Servlet container and can be easily embedded in devices, tools, frameworks, application servers, and clusters
- Wildfly – formerly known as JBoss AS, or simply JBoss, is a flexible and lightweight open-source application server authored by JBoss, now developed by Red Hat
- Oracle Weblogic Server – a Java EE application server currently developed by Oracle Corporation
- Glassfish – the reference implementation of Java EE and an open-source application server project started by Sun Microsystems for the Java EE platform and now sponsored by Oracle Corporation
- IBM WebSphere Application Server – offers a fast, flexible and secure Java application server runtime environment
- TomEE – an all-Apache Java EE 6 Web Profile certified stack where Apache Tomcat is top dog
- Undertow – a flexible performant fully embeddable web server written in java, providing both blocking and non-blocking API’s based on NIO. It’s sponsored by JBoss and is the default web server in the Wildfly Application Server
- Oracle Application Server – Oracle Internet Application Server provides a single integrated packaged solution of for middleware infrastructure including Oracle Containers for J2EE, Oracle Web Cache, Oracle HTTP Server, Oracle Forms, Oracle Reports, Oracle Portal and Oracle Discoverer
- Vert.x-Web – a toolkit for writing sophisticated modern web applications and HTTP microservices with Vert.x
- JOnAS – an open-source implementation of the Java EE application server specification, developed and hosted by the ObjectWeb consortium
- Apache2 – the world’s most used web server software
- GigaSpaces eXtreme Application Platform (XAP) – a distributed in-memory data-grid suited for high performance and low-latency transaction processing as well as real-time analytics use cases.
- Pivotal tc Server – provides enterprise users with a lightweight Java application server that extends Apache Tomcat for use in large-scale mission-critical environments